About us
(3)Plastic Deformability and Strength Evaluation of Silicon Based Hard Brittle Material (SiC)
(5)Multi-scale Modeling and Analysis of Solid Materials: Collaboration
between Molecular Dynamics and Macroscopic Particle Method (Peridynamics
Theory)
(6)Nano-scale Tribology and Plastic Deformation: The Effect of Nano-sized
texturing on Friction
(7)Computer Simulation Methodology for Dynamic behavior of Solid Materials
(8)Universality of Structures based on Mechanical Function: Development from Molecular Structures to the Concept of Tensegrity
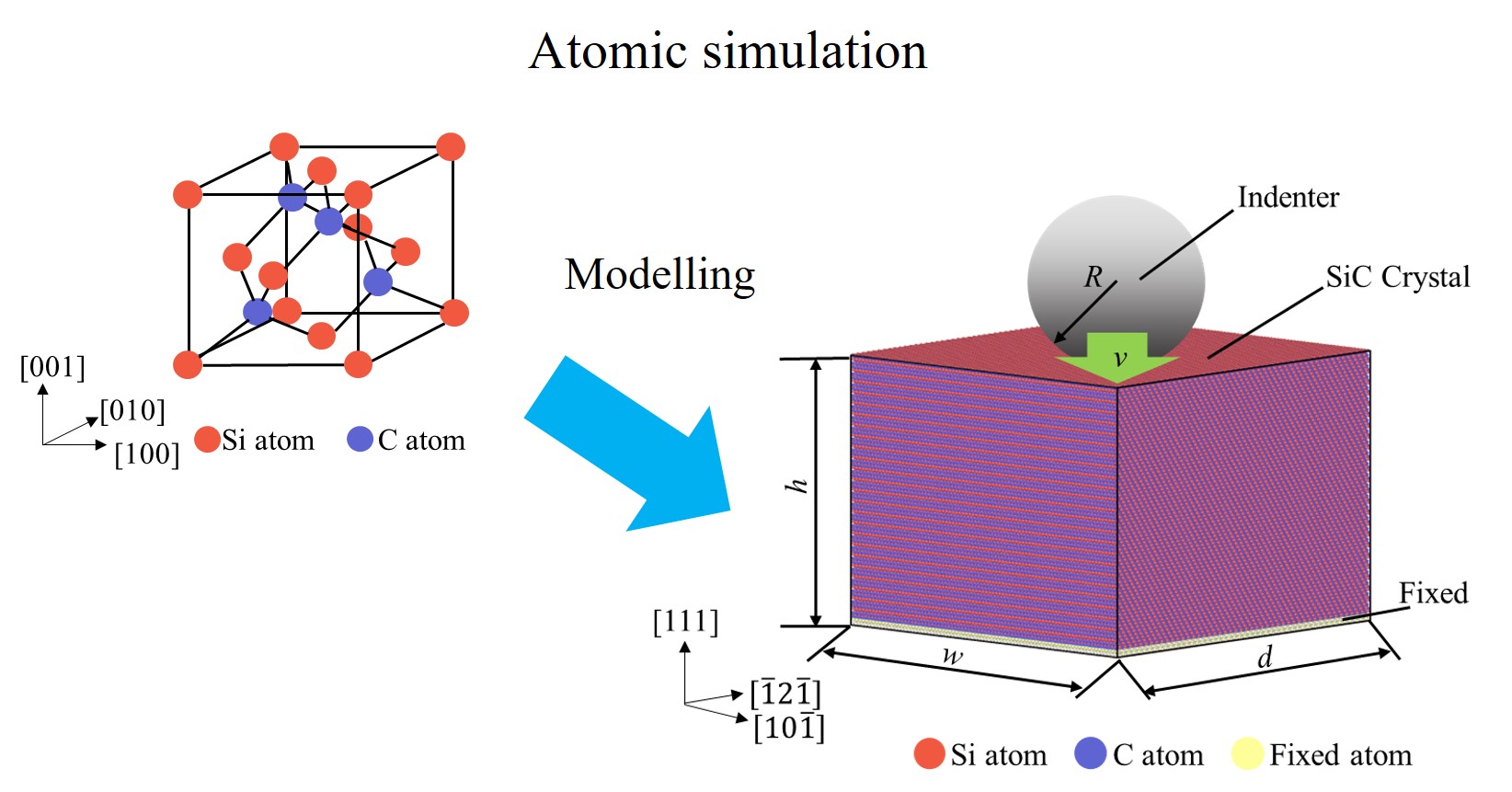
(3)Plastic Deformability and Strength Evaluation of Silicon Based Hard Brittle Material (SiC)
Due to the rapid progress of modern science and technology, problems about depletion of energy are concerned. To resolve these problems, there is an increasing need for energy conservation to obtain great economic and social effects with less energy. In promoting energy conservation, power electronics is trying to obtain an important role. Power electronics is a technology that freely controls voltage, current, frequency, power conversion using a power semiconductor and is used in a wide range of industrial equipment and automobiles. The performance limit of power electronics is said to be determined by the performance of semiconductors. Although much research has been conducted on silicon (Si), the mainstream of power semiconductors, it is said that no further performance can be expected. Therefore, great expectation is given to silicon carbide (SiC) having better physical properties than Si.