About us
(3)Plastic Deformability and Strength Evaluation of Silicon Based Hard Brittle Material (SiC)
(5)Multi-scale Modeling and Analysis of Solid Materials: Collaboration
between Molecular Dynamics and Macroscopic Particle Method (Peridynamics
Theory)
(6)Nano-scale Tribology and Plastic Deformation: The Effect of Nano-sized
texturing on Friction
(7)Computer Simulation Methodology for Dynamic behavior of Solid Materials
(8)Universality of Structures based on Mechanical Function: Development from Molecular Structures to the Concept of Tensegrity
(4)Mechanical Transmission in Hierarchical Structure of Biological Fibrillar Materials (Collagen / Cellulose Nano-sized Fibers): Twisting Force and Its Energy Transmission from Micro to Macro
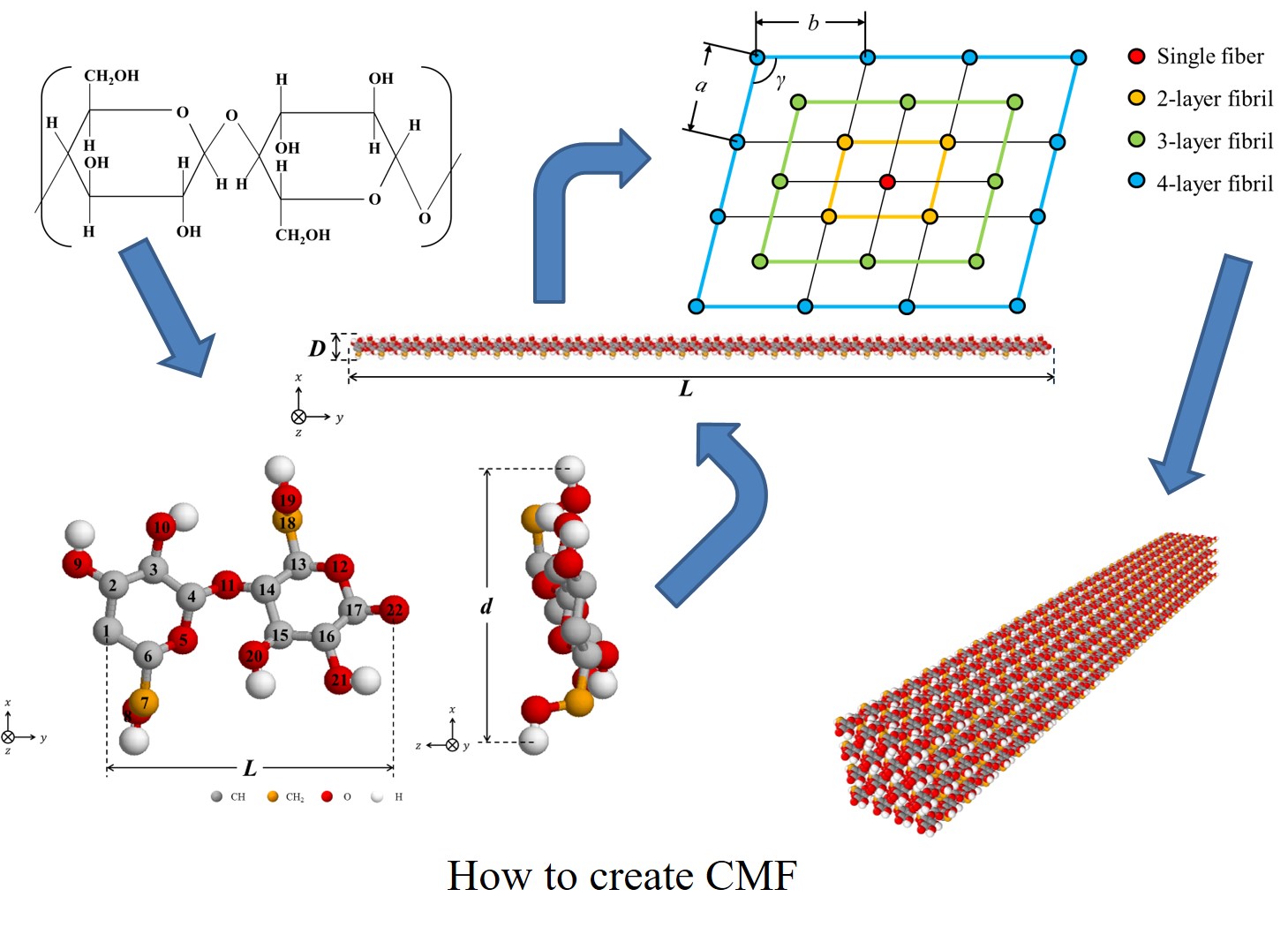
Cellulose is attracting attention as a new material as it is expected to
shift from petroleum-based manufacturing in recent years to bio-based manufacturing.
Cellulose is an aggregation of biological macromolecule (bio-polymers)
produced by photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide in plants. It
is constructed on a basic unit called cellulose microfibril (CMF), as observed
in cell wall of plants. CMF is constituted by a plurality of cellulose
monomers each of which are polymerized into a straight molecular chain.
A plurality of molecular chains are gathered and crystalized. Nanometer-sized
cellulose such as CMF is collectively called cellulose nanofiber (CNF).
Since CMF is fibrous, it is expected to be applied to fiber reinforced
plastics. Reinforced bicomponent fibers are often subjected to external
forces and are expected to bear mechanical loading, not only tension, but
also bending, twisting and their.