About us
(3)Plastic Deformability and Strength Evaluation of Silicon Based Hard Brittle Material (SiC)
(5)Multi-scale Modeling and Analysis of Solid Materials: Collaboration between Molecular Dynamics and Macroscopic Particle Method (Peridynamics Theory)
(6)Nano-scale Tribology and Plastic Deformation: The Effect of Nano-sized
texturing on Friction
(7)Computer Simulation Methodology for Dynamic behavior of Solid Materials
(8)Universality of Structures based on Mechanical Function: Development from Molecular Structures to the Concept of Tensegrity
(2)Atomistic Study on the Performance of Electrolytes in Lithium Ion Batteries(LIB): Evaluation of Li+ diffusion, viscosity and ionic conductivity
Among chemical ones, batteries that can be repeatedly charged and discharged
are called "secondary batteries". Currently, secondary batteries
are mainly marketed with lead storage batteries, nickel-metal hydride batteries,
and lithium ion batteries. In recent years, however, the demand for lithium-ion
batteries (LIB) is rapidly expanding with the miniaturization and weight
saving of equipment. Due to the spread of mobile terminals such as mobile
phones, smart phones, notebook computers, and owing to the advant of electric
vehicles, secondary batteries are required to be compact, lightweight,
large capacity, andrapidly rechargeable. A LIB is recognized as a secondary
battery that can satisfy these requirements.
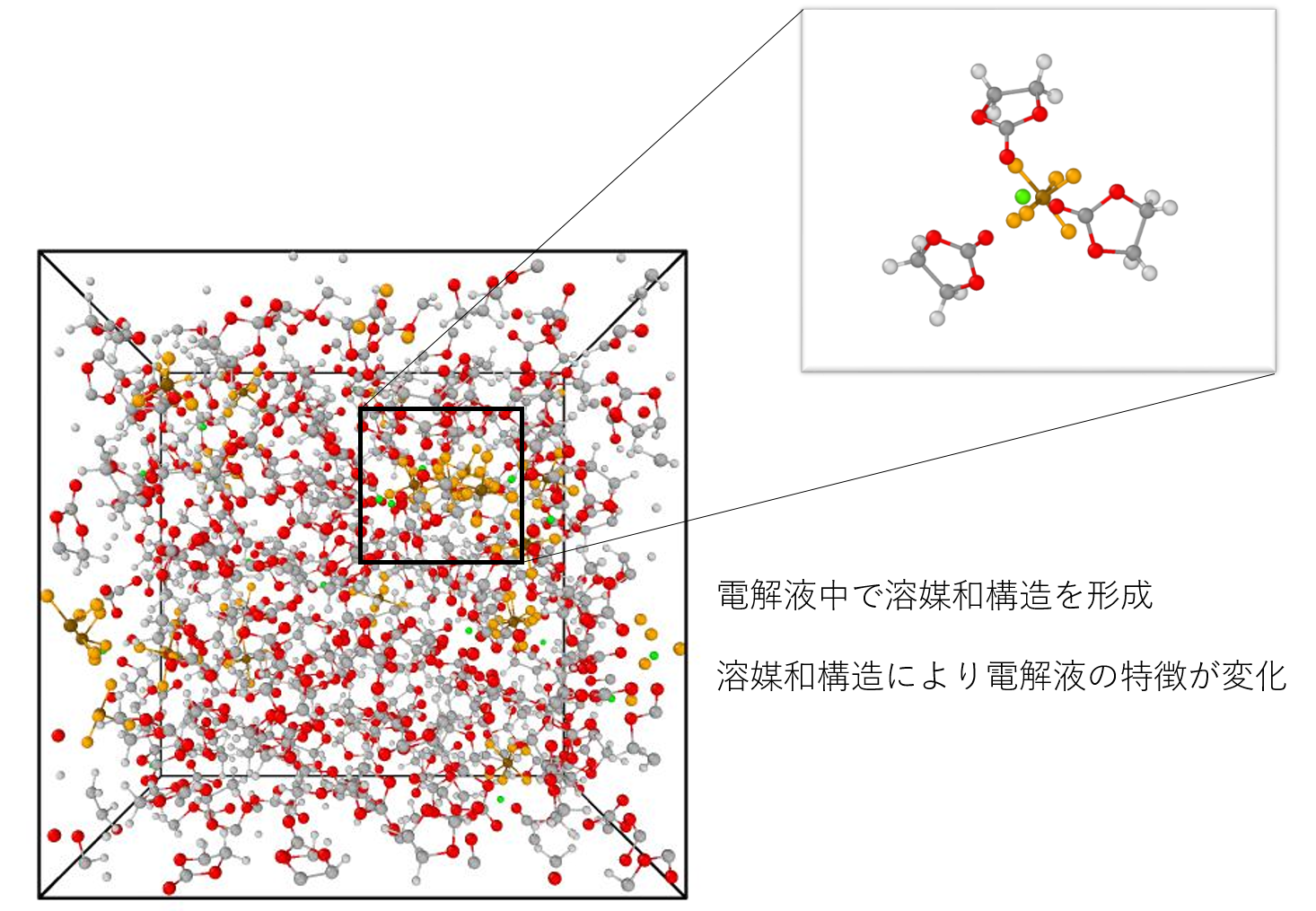
A LIB has higher energy density than other secondary batteries, so that
it is suitable for miniaturization and weight reduction. Besides, it has
a feature that its electric output with respect to weight is very large.
However, while it has a large capacity and high output, it has safety problems
such as ignition accidents. In addition to further improvement in the performance
of LIB, a solution method for safety problems is currently being sought.