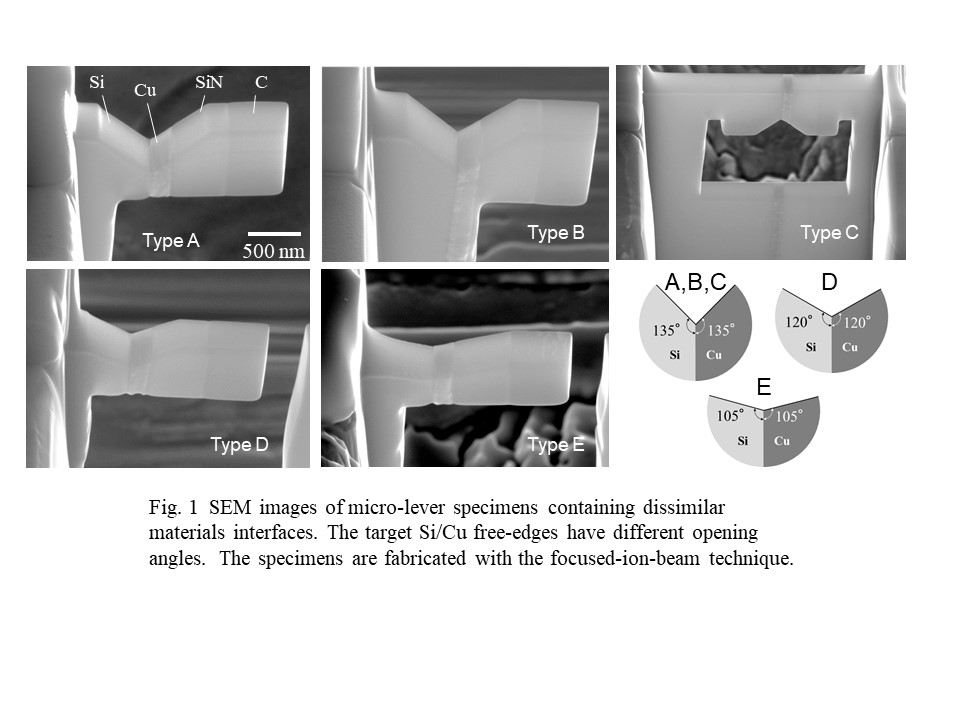
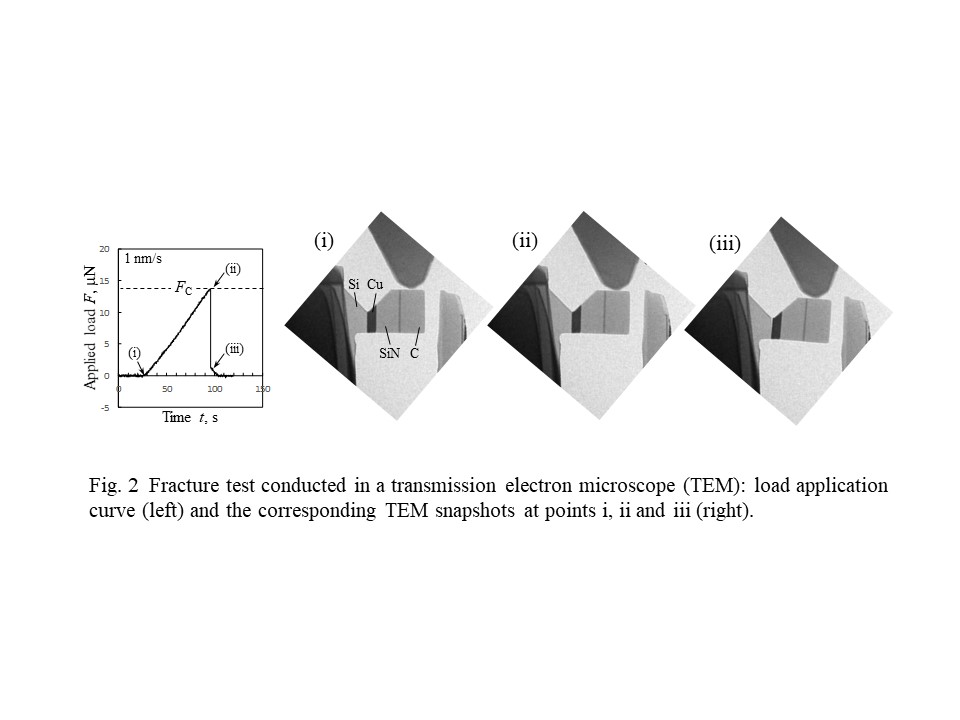
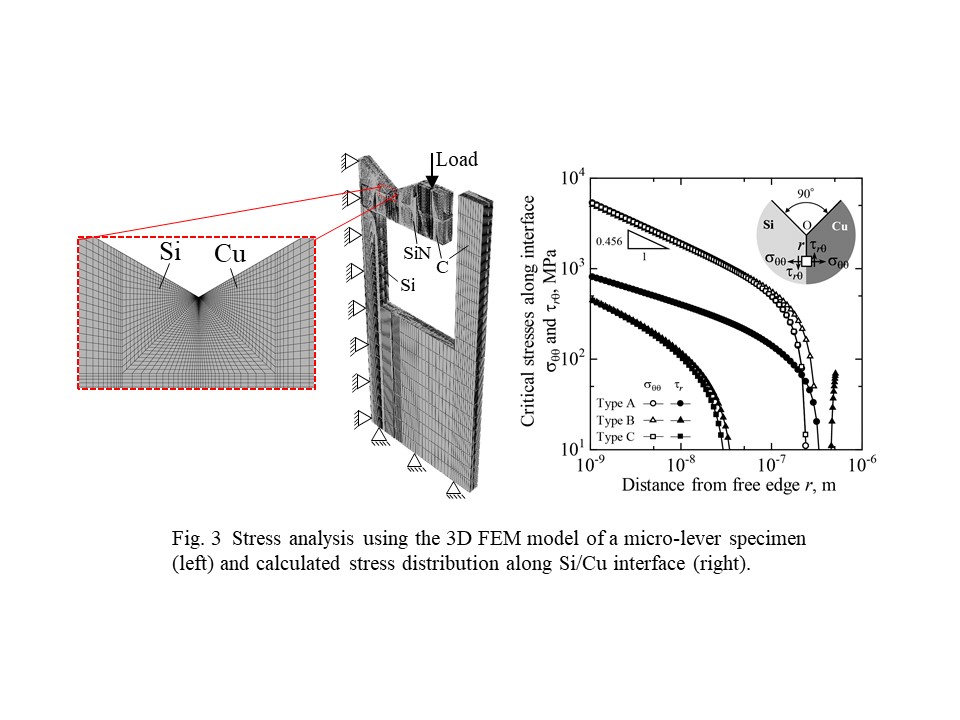
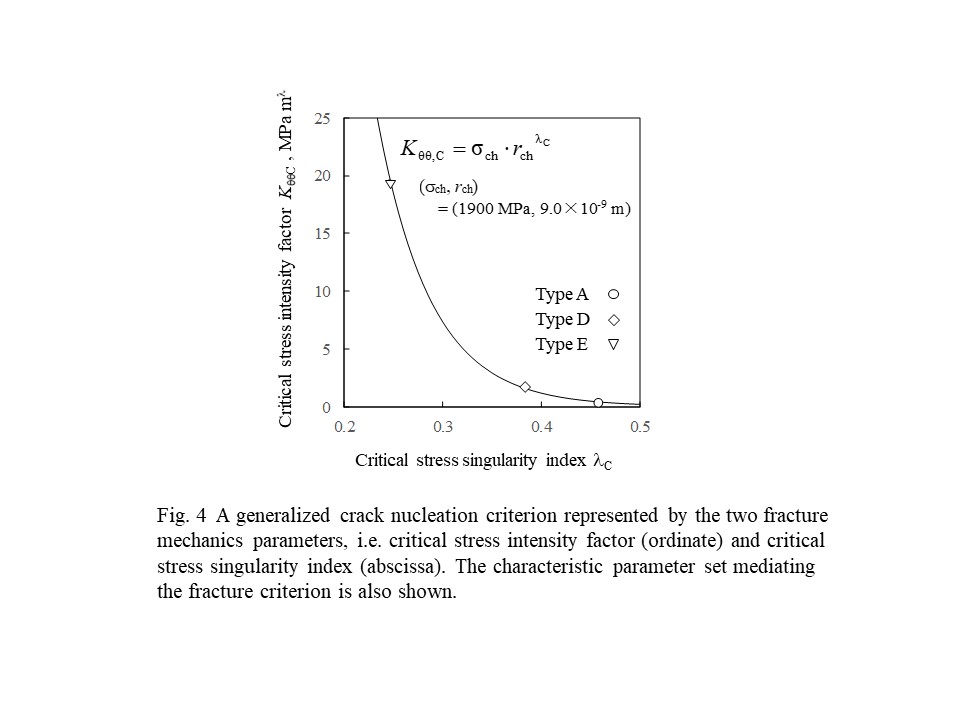
◆ Micro-materials fracture problem
Microdevices such as LSI and MEMS/NEMS are complex structures containing numerous numbers of micro-scale components. The structural integrity of the microdevices, just like an engine or a gear box, depends on the reliability of each minute component. It is therefore critically important to know the mechanical properties of micro-materials under various physical and/or chemical conditions.
We developed a special experimental technique to approach
this issue. Micro-specimens were fabricated with an ion-beam processing
method, and they were subjected to in situ deformation/fracture tests under
electron microscopy. The example shown here reveals that the fracture nucleation
from an interface edge can be successfully characterized by the fracture
mechanics approach even though the specimen dimension is very very small!
For more detail, see:
Y. Takahashi, K. Kishimoto, Y. Morii, S. Arai, K. Higuchi, S. Muto, Interfacial
fracture initiation strength of micro-scale Si/Cu components with different
geometries: Applicability of the fracture mechanics criterion, Engineering
Fracture Mechanics, Vol. 267, 2022, 108439 (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfracmech.2022.108439)
Related studies:
Y. Takahashi, I. Ashida, S. Arai, K. Higuchi, Y. Yamamoto, S. Muto, Interfacial
fracture strength evaluation of Cu/SiN micro-components: applicability
of the linear fracture mechanics criterion under a hydrogen environment,
International Journal of Fracture, Vol. 210, 2018, pp. 223–231 (https://doi.org/10.1007/s10704-018-0269-8)
Y. Takahashi, K. Aihara, I. Ashida, K. Higuchi, Y. Yamamoto, S. Arai, S.
Muto, N. Tanaka, Evaluation of interfacial fracture strength in micro-components
with different free-edge shape, Mechanical Engineering Journal, Vol. 3,
No. 6, 2016, ID: 16-00108
(https://doi.org/10.1299/mej.16-00108)
Y. Takahashi, S. Arai, Y. Yamamoto, K. Higuchi, H. Kondo, Y. Kitagawa,
S. Muto, N. Tanaka, Evaluation of interfacial fracture strength in micro-scale
components combined with high-voltage environmental electron microscopy,
Experimental Mechanics, Vol. 55, 2015, pp. 1047-1056 (https://doi.org/10.1007/s11340-015-0008-2)
Y. Takahashi, H. Kondo, H. Niimi, T. Nokuo, T. Suzuki, Fracture strength
analysis of single-crystalline silicon cantilevers processed by focused
ion beam, Sensors & Actuators: A. Physical, Vol. 206, 2014, pp. 81–87
(https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sna.2013.11.037)